InsureBook Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
Libraries used:
- JavaFX: Main GUI library
- JUnit5: Testing framework
- Jackson: JSON processing library (jackson-databind, jackson-datatype-jsr310)
- Gradle: Build automation tool
- Checkstyle: Code style checking
- JaCoCo: Code coverage
- Shadow: JAR packaging
UI Design:
- Original AddressBook-Level3 source code from SE-EDU initiative at https://github.com/se-edu/
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
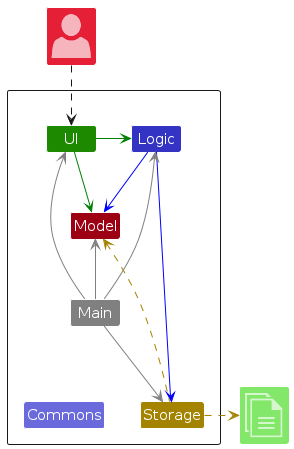
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of InsureBook.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of InsureBook.Logic: The command executor.Model: Holds the data of InsureBook in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
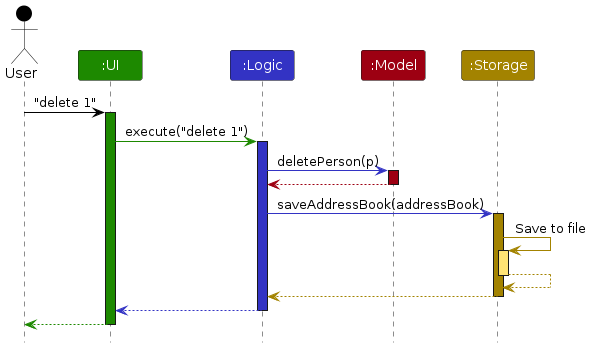
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
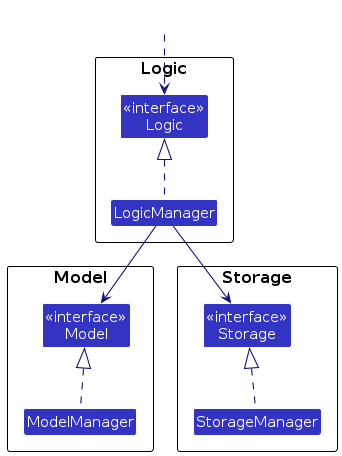
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
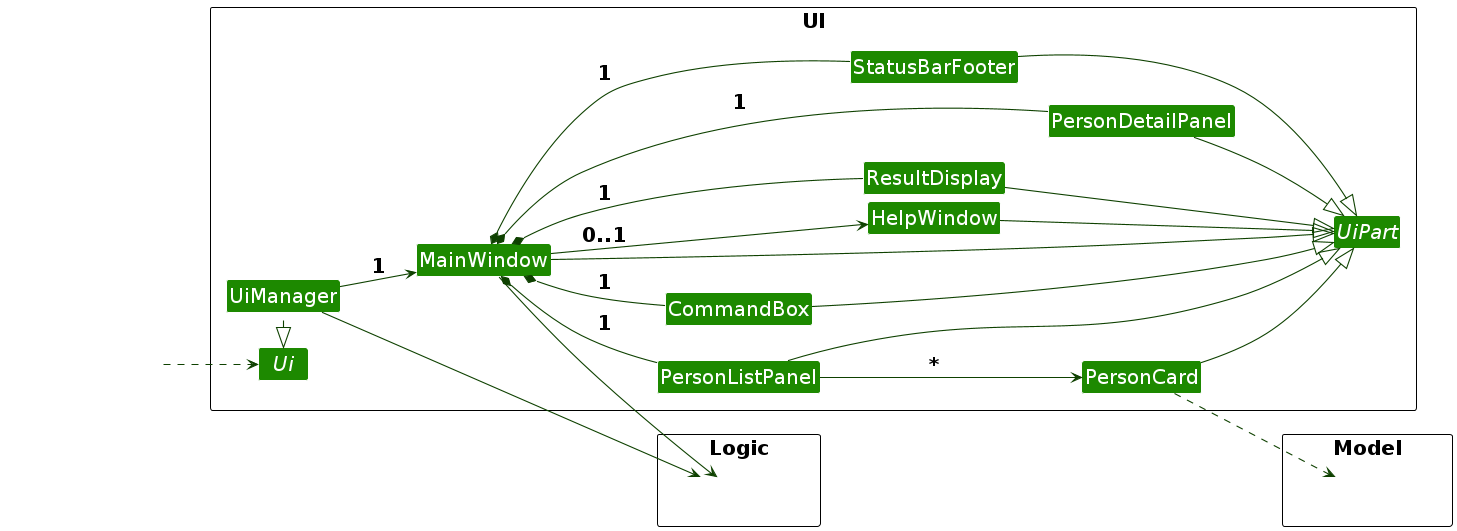
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, RenewalsTable, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonandPolicyobjects residing in theModel.
Person Card UI
The person card UI is implemented using the following components:
PersonListCard.fxml: Defines the layout of each person card, including:- Name and ID
- Contact information (phone, email, address)
- Tags
PersonCard.java: Controls the display of person information in the card:- Binds UI elements to person data
- Manages tag display
Person Details UI
PersonDetailPanel.fxml: Defines the layout of the display for a person's details, including:- Policy Number
- Renewal Date
- Policy Type
- Notes
PersonDetailPanel.java: Controls the display and updating of information of current selected person:- Binds UI elements (labels for policy number, renewal date, and notes) to the underlying person data model
- Formats the renewal date display with the prefix "Renewal date: " for clarity
- Dynamically updates the panel's content when a different person is selected in the main list
- Ensures that the Notes field, if it contains a lengthy string, wraps onto multiple lines without expanding the panel's width beyond its allocated space
The person card provides a compact view of all essential client information, making it easy for insurance agents to quickly access client details and track policy renewals. The renewal date is prominently displayed with a clear label to help agents quickly identify when policies need to be renewed.
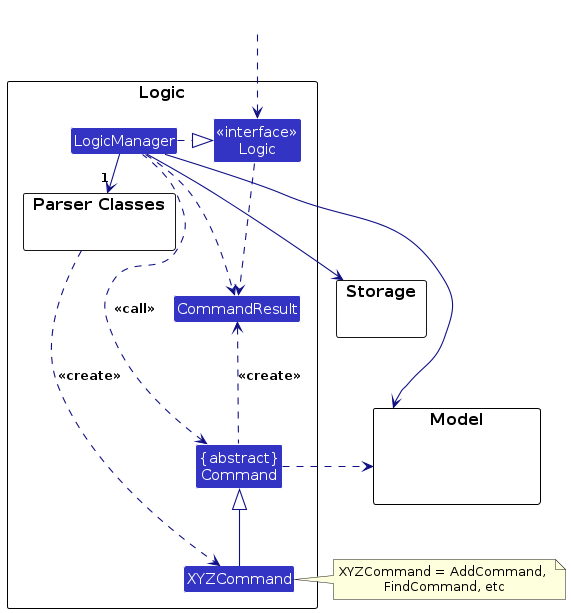
Logic component
API : Logic.java
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
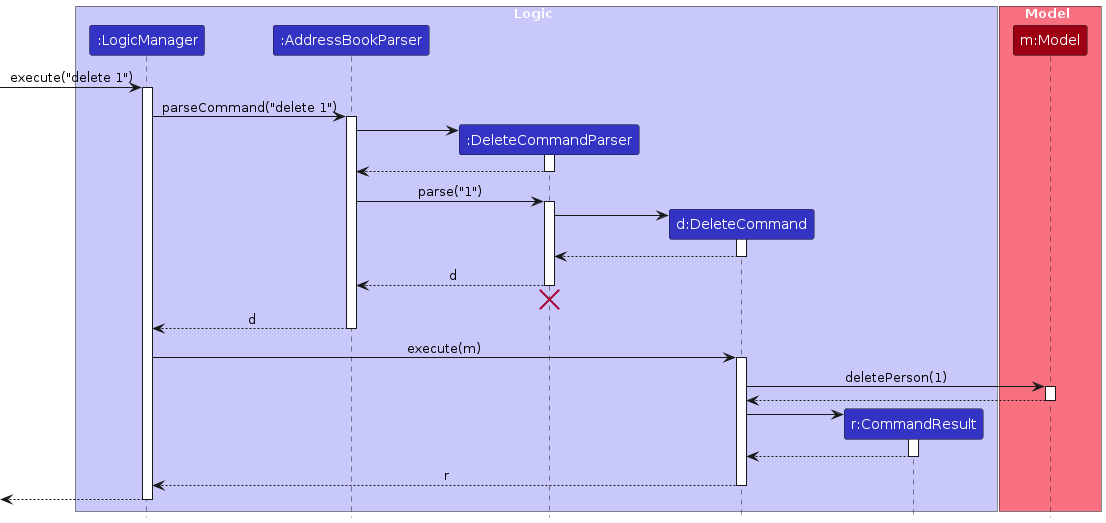
Note: The lifeline for DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a person).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
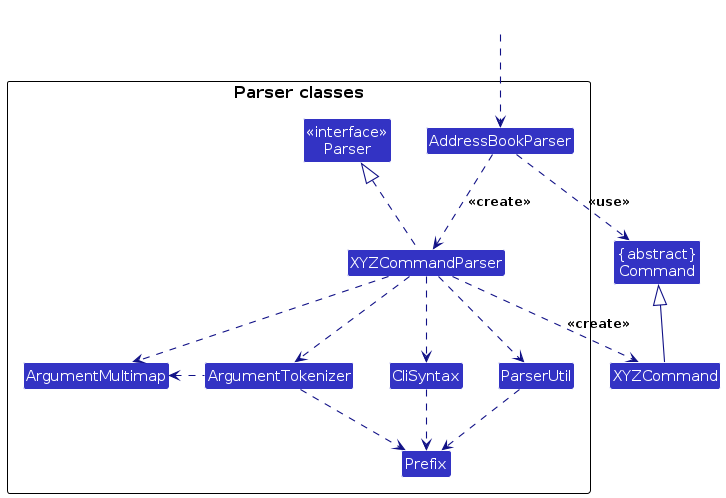
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
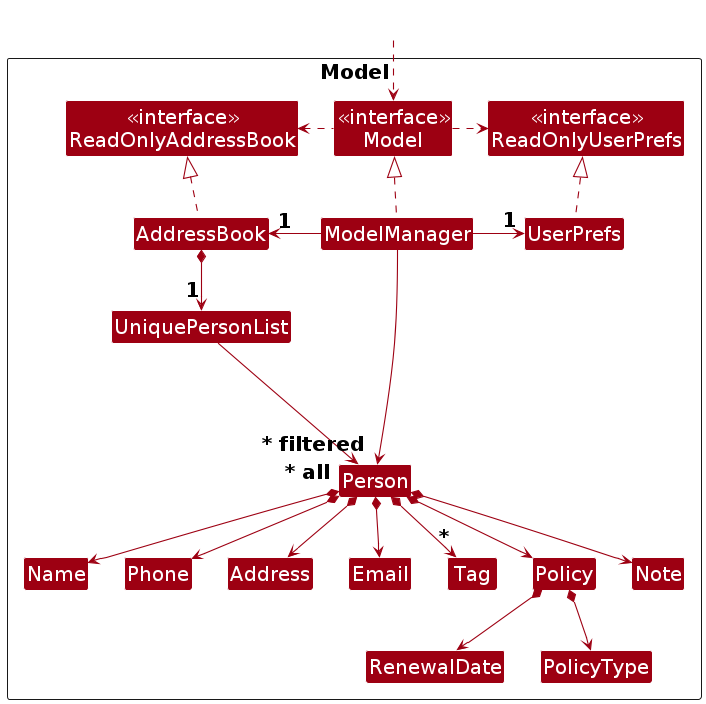
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - stores the currently 'selected'
Personobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user's preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
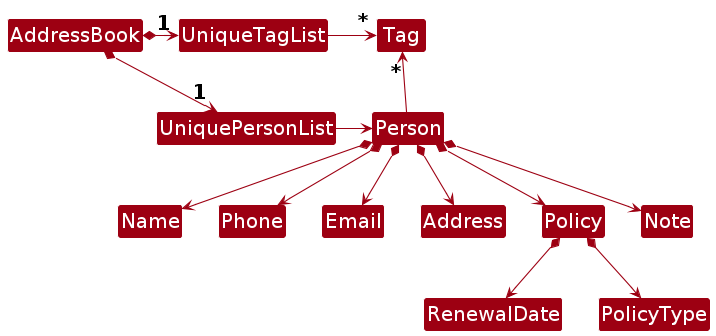
Note: An alternative (arguably, a more OOP) model is given below. It has a Tag list in the AddressBook, which Person references. This allows AddressBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Person needing their own Tag objects.
Storage component
API : Storage.java
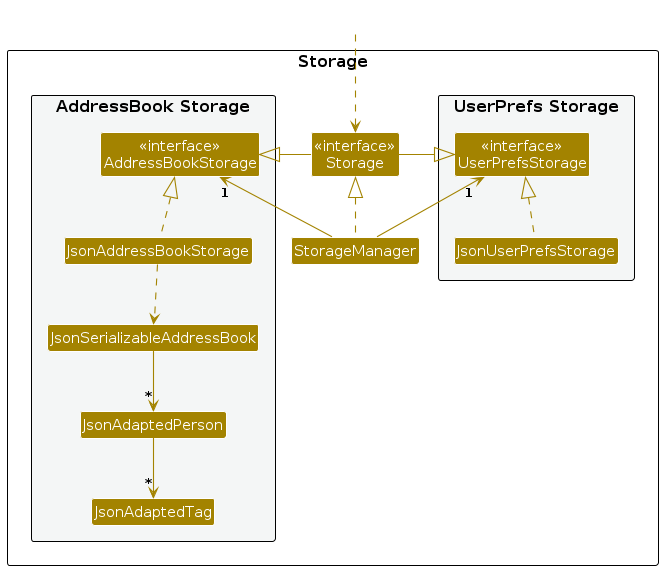
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package. These classes can be categorized into several groups:
Core Classes
Config: Stores configuration values used by the app, including log levels and file paths.GuiSettings: A serializable class containing GUI settings like window dimensions and coordinates.LogsCenter: Configures and manages loggers and handlers, supporting file and console logging.Version: Represents version information with major, minor, and patch numbers.
Utility Classes
AppUtil: Contains app-specific utility functions for image loading and argument validation.CollectionUtil: Provides utility methods for collection operations and null checking.FileUtil: Handles file operations like reading, writing, and path validation.JsonUtil: Manages JSON serialization/deserialization using Jackson library.StringUtil: Offers string manipulation utilities including case-insensitive search and integer validation.ConfigUtil: Provides access to configuration file operations.ToStringBuilder: Helps build consistent string representations of objects.
Index Classes
Index: Represents a zero-based or one-based index, facilitating index conversions between components.
Exception Classes
DataLoadingException: Represents errors during data loading from files.IllegalValueException: Signals that given data does not fulfill certain constraints.
These common classes provide essential functionality that is shared across different components of the application, promoting code reuse and maintaining consistency in how common operations are handled.
The classes are designed to be:
- Reusable across different components
- Independent of application-specific logic
- Focused on a single responsibility
- Well-documented with clear purpose
This organization helps maintain clean architecture by keeping common utilities separate from business logic while providing essential services to all components.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Policy Renewal Feature
The policy renewal feature allows insurance agents to track and manage policy renewals for their clients. It is implemented using the following components:
Policy Class
The Policy class represents an insurance policy and contains:
- Policy number (in format POL-XXX)
- Renewal date
- Methods to calculate days until renewal
ViewRenewalsCommand
The ViewRenewalsCommand allows users to view policies due for renewal within a specified number of days:
- Takes a parameter for number of days (1-365)
- Optional sort parameter (by name or date)
- Filters the person list based on policy renewal dates
- Updates the UI to show filtered results
Implementation
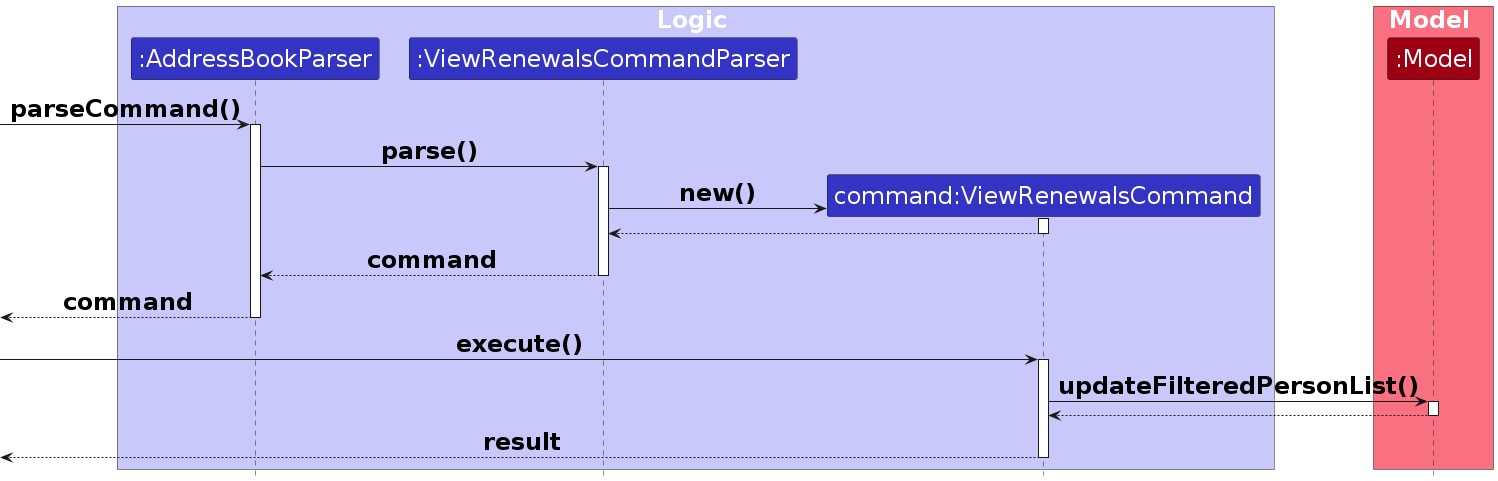
The renewal tracking mechanism is facilitated by the Policy class and the ViewRenewalsCommand. Here's how it works:
- When a user executes
viewrenewals n/30, the command is parsed byViewRenewalsCommandParser. - The parser validates the days parameter (must be 1-365) and optional sort parameter.
- A new
ViewRenewalsCommandis created with the validated parameters. - When executed, the command:
- Filters the person list to include only those with policies due within the specified days
- Updates the model's filtered person list
- Updates the renewals table in the UI
- Returns a command result with the number of matching entries
The following sequence diagram shows how the viewrenewals operation works:
Design Considerations
Aspect: How to calculate renewal due dates
Option 1 (Current Choice): Calculate days until renewal on demand
- Pros: More memory-efficient
- Cons: May affect performance if calculated frequently
Option 2: Store days until renewal as a field
- Pros: Faster retrieval
- Cons: Needs to be updated daily
Aspect: Where to implement filtering logic
Option 1 (Current Choice): In the command
- Pros: Keeps filtering logic with the command that needs it
- Cons: Logic may be duplicated if needed elsewhere
Option 2: In the Model
- Pros: Centralizes filtering logic
- Cons: Makes the Model more complex
Renewal Date Update Feature
The renewal date update feature allows insurance agents to directly update a client's policy renewal date by specifying the policy number, without needing to find the client's index in the list. This feature streamlines the renewal date management process.
Implementation
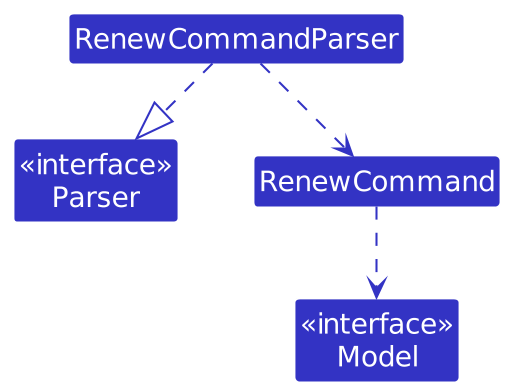
The renewal date update functionality is implemented through the RenewCommand class, which follows the command pattern used throughout the application. The feature is primarily made up of the following components:
RenewCommand- Executes the updating of a renewal date for a client with a specific policy numberRenewCommandParser- Parses and validates the user input into a RenewCommand object
The following class diagram shows the structure of the Renew Command:
The feature works through the following process flow:
- The user enters a command in the format
renew pol/POLICY_NUMBER r/RENEWAL_DATE. - The
LogicManagerpasses the command string toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParseridentifies the command as arenewcommand and delegates toRenewCommandParser.RenewCommandParserextracts and validates:- Policy number (must be a valid policy number format)
- Renewal date (must be a valid date in DD-MM-YYYY format)
LogicManagercalls theexecute()method of the command object.- The
RenewCommand:- Filters the list of persons to find those with the specified policy number
- Validates that exactly one match is found (not zero, not multiple)
- Creates a new
Personwith the updated renewal date while preserving other fields (including policy type) - Updates the model with the new
Personobject - Returns a
CommandResultwith a success message
The following sequence diagram shows how the renew operation works:
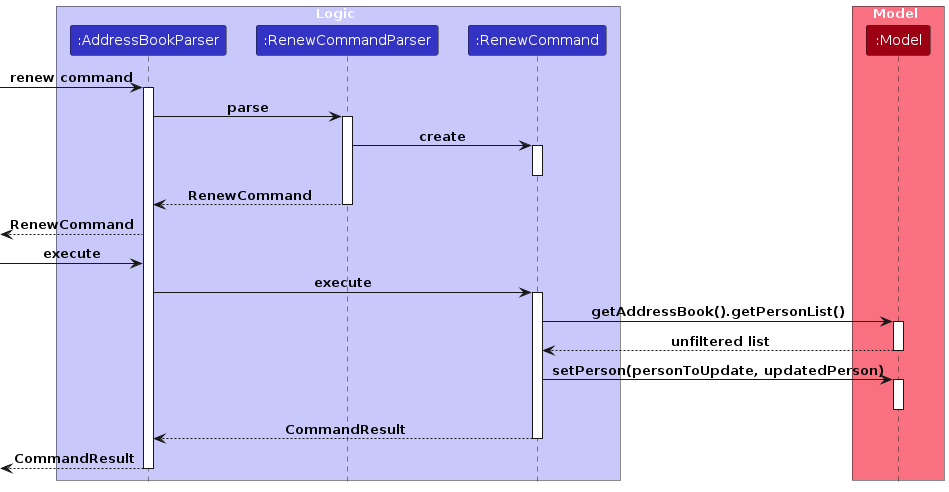
Design Considerations
Aspect: How to identify the client to update:
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use policy number as identifier.
- Pros: More intuitive for insurance agents who often reference clients by policy number.
- Cons: Requires handling cases where multiple clients have the same policy number.
Alternative 2: Use client index in the displayed list.
- Pros: Consistent with other commands like
editanddelete. - Cons: Less convenient as agents need to find the index first.
- Pros: Consistent with other commands like
Aspect: Error handling for duplicate policy numbers:
Alternative 1 (current choice): Show error and suggest using
editcommand.- Pros: Prevents unintended updates to the wrong client.
- Cons: Less convenient when there are duplicate policy numbers.
Alternative 2: Update all clients with matching policy numbers.
- Pros: More convenient if updating all matching policies is the intended action.
- Cons: High risk of unintended updates; insurance operations generally require precision.
Find Persons Feature
The FindCommand allows users to search for persons in the address book by specifying various attributes. This feature is enhanced to support searching across all person attributes, providing a flexible and comprehensive search capability.
FindCommand
The FindCommand enables users to search for persons based on any attribute, such as name, address, phone number, email, tags or policy number. It is implemented using the following components:
FindCommand: Executes the search operation.FindCommandParser: Parses and validates the user input into a FindCommand object.FindPersonPredicate: A predicate that evaluates whether a person matches the search criteria.
FindPersonPredicate
The FindPersonPredicate class is responsible for evaluating whether a person matches the search criteria. It is implemented as follows:
Attributes: The predicate stores the search criteria for each attribute in their own predicate object. Evaluation:
- The
testmethod checks if a person matches the search criteria by evaluating each attribute. - It supports partial matches and is case-insensitive.
- For each attribute, it checks if the person's attribute contains the search value.
The following class diagram shows the structure of the FindPersonPredicate:
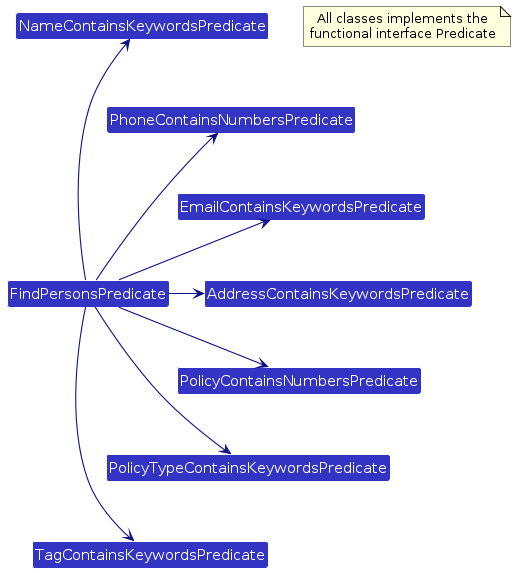
The following partial sequence diagram shows how the test operation works:
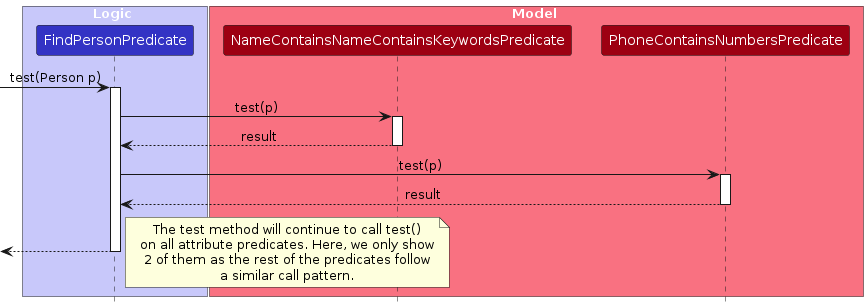
Design Considerations
Aspect: How to handle multiple search criteria
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Combine all criteria using logical OR.
- Pros: Ensures that a person is considered a match if any of the specified attributes match, providing more flexible search results.
- Cons: May result in more matches if multiple criteria are specified.
- Alternative 2: Use logical AND to require all criteria to match.
- Pros: Ensures that all specified attributes must match, providing precise search results.
- Cons: May result in fewer matches if multiple criteria are specified.
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Combine all criteria using logical OR.
Aspect: Case sensitivity and partial matches
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Use case-insensitive and partial matches.
- Pros: More user-friendly and flexible, accommodating various input styles.
- Cons: May result in unintended matches if search values are too general.
- Alternative 2: Case-sensitive with exact matches
- Pros: Highest precision in search results, ideal for technical/specialized searches and minimizes irrelevant matches
- Cons: Most restrictive option for users, steeper learning curve and requires perfect knowledge of stored data format
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Use case-insensitive and partial matches.
Filter Command
The filter command allows users to view policies due for renewal within a specified date range. This helps agents proactively manage upcoming renewals.
- Takes two parameters, startDate and endDate to specify the date range
- Optional sort parameter (by date or name); defaults to date
- Filters the person list based on policy renewal dates
- Updates the UI to show filtered results, and the filter specified when calling this command
Implementation
FilterDateCommand: Executes the filtering and sorting of clients based on the provided date range and sort order.FilterDateCommandParser: Parses and validates the user input into a FilterCommand object.
The following class diagram shows how the filter command updates the UI:
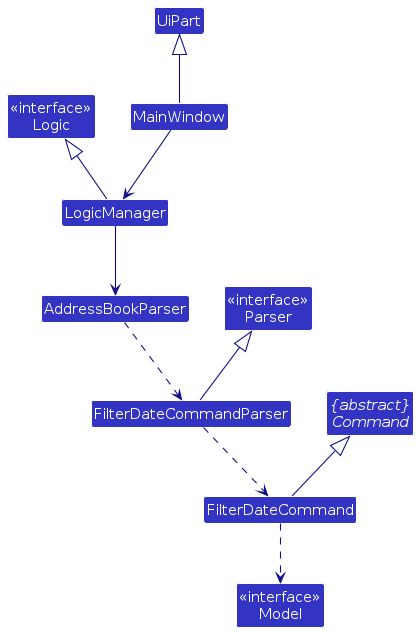
The following sequence diagram shows how the filter command works:
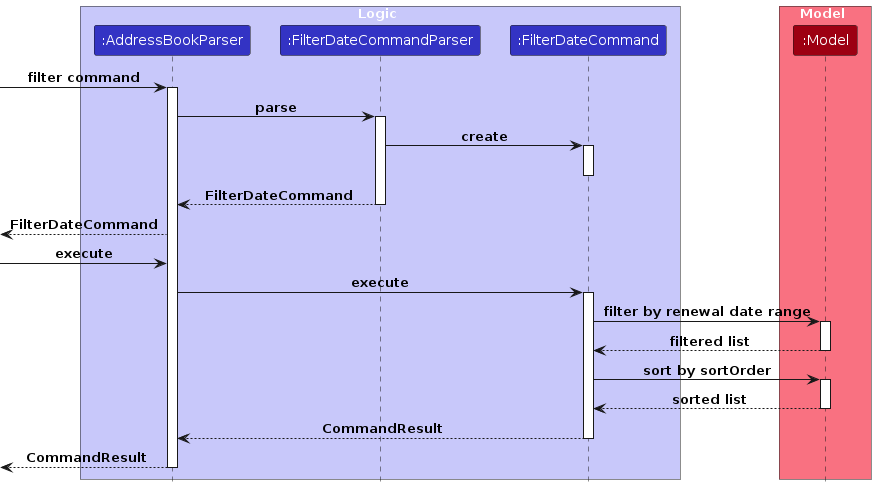
Design Considerations
Aspect: Sort Order Options
Current Choice: Accept only date or name as valid sort orders, case-insensitive. Defaults to date when not specified.
- Pros: Simple and supports the most common use cases.
- Cons: Doesn't support complex custom sorting (e.g., by policy number or tags).
Alternative: Expand to include additional sort fields.
- Pros: More customization.
- Cons: Increases complexity in command parsing and validation.
Aspect: Type for startDate and endDate
Current Choice: Uses LocalDate for variables startDate and endDate.
- Pros: Simple and has predefined methods.
- Cons: Might be difficult to add custom fields or methods.
Alternative: Use RenewalDate class.
- Pros: More customization.
- Cons: Increases coupling with the Renewal Date class which may not be tailored for the specific needs of the FilterDateCommand.
Policy Type Feature
Current Implementation
The policy type feature enhances the insurance management capabilities of the application by allowing users to categorize policies into specific types (Life, Health, Property, Vehicle, and Travel). This helps insurance agents quickly identify and manage different types of policies.
The implementation consists of the following key components:
PolicyTypeEnum - Defines the available policy types and provides utilities for validation and conversion.public enum PolicyType { LIFE, HEALTH, PROPERTY, VEHICLE, TRAVEL; public static PolicyType fromString(String type) { ... } public static boolean isValidPolicyType(String test) { ... } }PolicyClass Extension - The existingPolicyclass has been enhanced to include aPolicyTypefield.public class Policy { // Existing fields public final String policyNumber; public final RenewalDate renewalDate; // New field private final PolicyType type; // Constructors that handle policy type public Policy(String policyNumber, String renewalDate, String type) { ... } // Getter for policy type public PolicyType getType() { ... } }Command Parsers - The parsers for
AddCommand,EditCommand, andFindCommandhave been updated to recognize and process the policy type prefix (pt/).UI Components - The
PersonCardandRenewalsTableUI components have been modified to display the policy type.Predicate for Searching - A
PolicyTypeContainsKeywordsPredicateclass has been added to support searching by policy type.
Design Considerations
Aspect: Implementation of Policy Types
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use an enumeration to represent policy types.
- Pros: Type safety, easy validation, prevents invalid policy types.
- Cons: Less flexible if new types need to be added (requires code changes).
Alternative 2: Use a string field without constraints.
- Pros: More flexible, users can add any type they want.
- Cons: Less type safety, harder to validate, potential for inconsistent data (e.g., "Health" vs "health").
Aspect: Storage of Policy Type
Alternative 1 (current choice): Store as part of the Policy object.
- Pros: Logical grouping, keeps policy information together.
- Cons: Increases complexity of the Policy class.
Alternative 2: Store as a separate field in the Person object.
- Pros: Simpler Policy class.
- Cons: Less logical grouping, policy information is split between different attributes.
Example Usage
The following sequence diagram shows how adding a person with a policy type works:
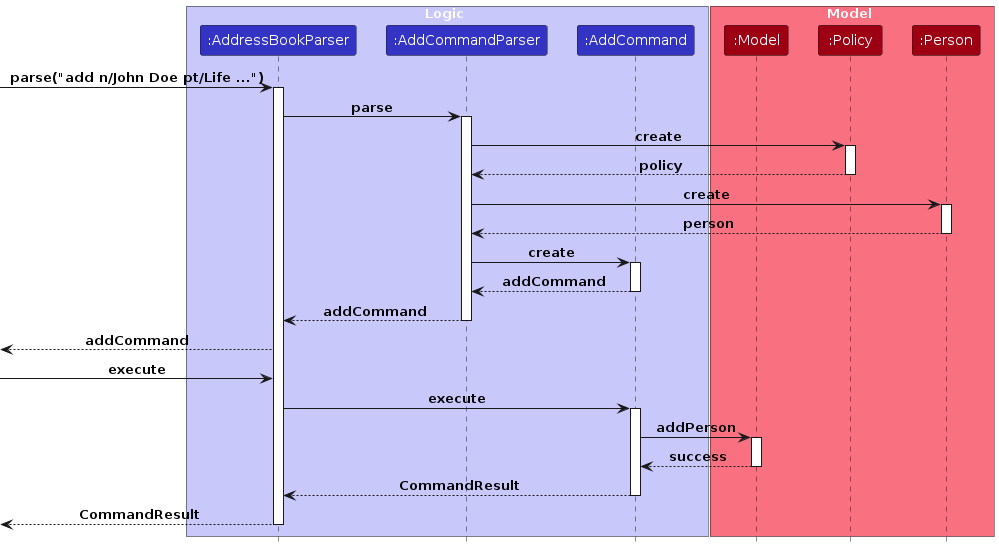
When the user adds a new person with a policy type:
- The
AddCommandParserparses the command including the policy type prefix. - A new
Policyobject is created with the specified policy type. - This
Policyis included in the newPersonobject. - The Model stores the new person and returns success.
- A
CommandResultis returned to indicate success.
The UI components will automatically update to reflect the changes in the Model.
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- Insurance Agents who need to keep track of Customers / Potential Customers
- Moderate Tech saviness.
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: It solves the issue of managing a large clientele by simplifying client tracking, automating follow-ups, and staying organized. By using InsureBook, insurance agents can focus more on growth and client retention, rather than spending more time on admin tasks and more time on sales.
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | Insurance Agent | add new clients | reach out to them when needed |
* * * | Insurance Agent | view a list of clients | quickly access current and potential clients |
* * * | Insurance Agent | update client information | ensure records remain accurate |
* * * | Insurance Agent | delete a client entry | remove outdated clients |
* * * | Insurance Agent | search for a client | quickly find them through their details |
* * * | Insurance Agent | filter clients by renewal date | prioritize follow-ups effectively |
* * * | Insurance Agent | tag clients for sorting & search | organize and categorize my clients |
* * * | Insurance Agent | set reminders for renewals | never miss important deadlines |
* * * | Insurance Agent | persist client data | ensure no data is lost |
* * * | Insurance Agent | filter and sort clients by tags | manage clients more efficiently |
* * | Insurance Agent | add notes to a client's profile | remember key details about them |
* * | Insurance Agent | sort my clients by tag | so that I can quickly rank my clients based on the number of tags they have. |
Use Cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the Client Management System and the Actor is the Insurance Agent, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: Add a new client
MSS
Insurance Agent inputs the
addcommand with client details.System validates and saves the new client.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The provided details are invalid.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. A duplicate client is detected.
- 2b1. System detects one of the following duplicate conditions:
- The same policy number exists
- The same name and email combination exists
- The same name and phone number combination exists
- 2b2. System shows a specific error message indicating which duplicate condition was matched.
- 2b3. System rejects the addition.
- 2b4. Use case resumes at step 1.
- 2b1. System detects one of the following duplicate conditions:
2c. User adds duplicate tag.
- 2c1. System ignores the duplicate and does not repeat the duplicate tag.
Use case: View a list of clients
MSS
Insurance Agent inputs the
listcommand.System displays all stored clients in alphabetical order.
Use case ends.
Use case: Update client information
MSS
Insurance Agent inputs the
editcommand with the client index and new details.System validates and updates the client information.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Provided details are invalid.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. Client does not exist.
- 2b1. System shows an error message.
2c. Update would create a duplicate client.
- 2c1. System detects that the update would result in:
- A policy number that matches another client
- A name and email combination that matches another client
- A name and phone number combination that matches another client
- 2c2. System shows a specific error message indicating which duplicate condition was matched.
- 2c3. System rejects the update.
- 2c4. Use case resumes at step 1.
- 2c1. System detects that the update would result in:
2c. User adds duplicate tag.
- 2c1. System ignores the duplicate and does not repeat the duplicate tag.
Use case: Delete a client
MSS
Insurance Agent inputs the
deletecommand with the client identifier.System deletes the specified client.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. The given index is invalid.
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Clear all client data
MSS
- Insurance Agent types the command to clear all client data.
- System permanently deletes all stored client data immediately.
Use case ends.
Warning:
- This action is irreversible.
- All client data will be permanently lost.
Use case: Find a client
MSS
Insurance Agent inputs the
findcommand with specific criteria.System displays matching clients.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. No matching clients found.
- 2a1. System shows "0 persons listed!"
- 2a2. Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. User searches for duplicate tag in 'find' command.
- 2b1. System ignores the duplicate searched tag.
- 2b2. Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Filter and sort clients by tags
MSS
Insurance Agent inputs the
filtercommand with specific criteria and tags, and adds a sort by either name or tag.System displays a list of clients with the matching tags.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. No clients match the specified tags.
- 2a1. System shows "0 persons listed!"
- 2a2. Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. User searches for duplicate tag in 'find' command.
- 2b1. System ignores the duplicate searched tag.
- 2b2. Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: View upcoming renewals within a period
MSS
- Insurance Agent inputs the
viewrenewalscommand with an optional timeframe and sort order. - System displays policies due for renewal within the specified period.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Provided period is not a valid positive integer.
- 2a1. System defaults to 30 days and shows clients that match the 30 day renewal criteria.
- 2a2. Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. No policies match the specified period.
- 2b1. System shows "No upcoming renewals within [X] days.", where X is the number of days requested [30 default otherwise].
- 2b2. Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: View policy renewals within a date range
MSS
- Insurance Agent inputs the
filtercommand with start date, end date, and optional sort order. - System validates and displays policy renewals within the specified range.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Date range is invalid (end date is before start date).
- 2a1. System shows an error message.
- 2a2. Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. No policies match the provided date range.
- 2b1. System shows "No renewals found between [STARTDATE] and [ENDDATE]."
- 2b2. Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Update policy renewal date
MSS
- Insurance Agent inputs the
renewcommand with policy number and renewal date. - System validates and updates the renewal date.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Provided policy number does not exist.
- 2a1. System shows an error message that shows that policy number does not exist.
- 2a2. Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. Provided renewal date is invalid.
- 2b1. System shows an error message indicating date format requirements.
- 2b2. Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Persist client data
MSS
System automatically saves client data when changes are made.
Use case ends.
Use case: View help information
MSS
Insurance Agent inputs the
helpcommand.System opens a new window with a link to the User Guide.
Use case ends.
Use case: Exit the Client Management System
MSS
Insurance Agent inputs the
exitcommand.System terminates the session safely.
Use case ends.
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
17or above installed. - The system should be intuitive for insurance agents who may not be tech-savvy but are proficient at typing.
- Should be able to hold up to 1000 clients without noticeable sluggishness in performance.
- Should start up and be ready to use in under 2 seconds on a modern machine.
- Should be deliver response to user within 5 seconds of user carrying out the command.
- Should not require an internet connection to function.
- A user with above-average typing speed should be able to accomplish most tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Client data should persist even if the system shuts down unexpectedly.
- All error messages should be clear and actionable to help users recover quickly from mistakes.
Glossary
- Insurance Agent: The primary user of InsureBook: someone who manages and tracks client details, insurance policies, and renewals.
- Client: An individual whose information is stored in InsureBook. This includes their name, contact details, address, associated policies, and optional notes or tags.
- Policy: An insurance agreement linked to a client, which includes details like policy number, type, and renewal date.
- Policy Number: A unique numeric code that identifies a client's insurance policy. It must be different for each policy entered.
- Renewal Date: The date by which a client's policy must be renewed to stay active. This date is managed using
renew,viewrenewals, andfilter. - Policy Type: The category of a policy. Supported types include:
Life,Health,Property,Vehicle, andTravel. - Tag: A label added to clients for categorization or filtering purposes. For example,
t/vip,t/family, ort/lead. - User Interface (UI): The graphical layout and interactive components (e.g., windows, panels, forms) through which the insurance agent interacts with the system.
- Logic: The system component that processes user commands by coordinating between the UI and the data model.
- Model: The component that holds all the client and policy data in memory and represents the business entities.
- Storage: The component responsible for reading from and writing data to disk, ensuring data persists between sessions.
- Command: A typed instruction entered in the command box (e.g.,
add,edit,viewrenewals) that tells InsureBook what action to perform. - Command Parser: The module that interprets raw user input and converts it into a structured command object.
- Command Result: The outcome returned after a command is executed, including success confirmations or error messages.
- ObservableList: A data structure that automatically notifies the UI of changes in the model, ensuring real-time updates.
- Duplicate Entry: An entry that conflicts with existing data due to matching policy number, name + email, or name + phone. These entries are rejected to maintain data accuracy.
- Tag: A custom keyword used to categorize clients for sorting and filtering.
- Data Persistence: The capability of the system to save client and policy data so that information is retained across sessions.
- Mainstream OS: Operating systems such as Windows, Linux, Unix, and MacOS.
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Note: These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing.
Launch and shutdown
Initial launch
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
Use the
java -jar InsureBook.jarcommand to run the application.
Note: The Application will default to full-screen mode.
Adding a person
Adding a person into InsureBook
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
listcommand. InsureBook default sample list used.Test case:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 pol/999999 pt/Life r/31-12-2025 note/Basketball Player
Expected: Person added successfully into the end of the list, and their details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
add n/Betsy Crowe t/friend pol/654321 pt/Health e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/91234567 t/criminal
Expected: Person added successfully into the end of the list, and their details are displayed in the status message.Incorrect add commands to try:
add n/bobby,...
Expected: Person not added into the list, error details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.
Adding a person with duplicate policy number into InsureBook
Prerequisites: There exist a person with the same policy number in the list as the person that is being added.
Test case:
add n/Alan Lim p/98761234 e/alan@gmail.com a/alan drive pol/123456
Expected: Person not added into the list, error details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.
Editing a person
Editing an existing person from InsureBook
Prerequisites: There is at least 1 person in the list.
Test case:
edit 1 n/Alexander e/alexander@example.com
Expected: Person edited successfully, and their details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
edit 0
Expected: No person is edited. Error details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.Other incorrect edit commands to try:
edit,edit x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Editing an existing person's policy number to a number that is used already from InsureBook
Prerequisites: There exists a person in the list whose policy number match the policy number that is being edited into.
Test case:
edit 2 pol/123456
Expected: No person is edited. Error details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.
Deleting a person
Deleting an existing person while all persons are being shown
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
listcommand. Multiple persons in the list.Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First person is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted person are displayed in the status message.Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No person is deleted. Error details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Updating a policy renewal date
Updating a policy renewal date of a person
Prerequisites: There exist a person in the list with the policy number that is being tested and the rd/RENEWAL_DATE must be later than the current date e.g. 20-04-2025.
Test case:
renew pol/234567 r/31-12-2025
Expected: Person policy renewal date updated successfully, and details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
renew pol/234567 r/2025-06-11
Expected: No person policy renewal date updated. Error details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
renew,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Updating a policy renewal date of a person whose policy number does not exist
Prerequisites: Every person in the list has a policy number that does not match what is being tested and the rd/RENEWAL_DATE must be later than the current date e.g. 20-04-2025.
Test case:
renew pol/969696 r/06-11-2025
Expected: No person policy renewal date updated. No policy was found, details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.
Viewing upcoming policy renewals
Viewing upcoming policy renewals from the list
Prerequisites: There is at least 1 person in the list.
Test case:
viewrenewals
Expected: Shows persons with upcoming renewals in the next 30 days, sorted by date, and details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
viewrenewals n/300 s/name
Expected: Shows persons with upcoming renewals in next 300 days, sorted by name, and details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
viewrenewals n/0
Expected: No persons with upcoming renewals shown. Error details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
viewrenewals n/366,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Viewing upcoming policy renewals for policy that falls after the specified test day.
Prerequisites: Every person in the list has a policy renewal date that falls after the specified test day.
Test case:
viewrenewals n/60 s/name
Expected: No persons with upcoming renewals shown, and details are displayed in the status message.
Viewing policy renewals in date range
Viewing policy renewals in a filtered range from the list
Prerequisites: There is at least 1 person in the list with renewal date within the sd/START_DATE and ed/END_DATE.
Test case:
filter sd/20-04-2025 ed/20-12-2026
Expected: Show a filtered list with persons with renewal dates within the provided range, sorted by date, and details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
filter sd/20-04-2025 ed/20-12-2026 s/name
Expected: Show a filtered list with persons with renewal dates within the provided range, sorted by name, and details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
filter sd/20-04-2025
Expected: list of person is not filtered. Error details are displayed in the status message and command entered stays in the command box.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
filter,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Viewing policy renewals in a filtered range from the list for a policy that falls outside the specified test date range.
Prerequisites: Every person in the list has a policy renewal date that falls outside the specified test date range.
Test case:
filter sd/20-04-2025 ed/20-05-2025
Expected: No persons shown, and details are displayed in the status message.
Listing all persons
Viewing all persons in the list
Prerequisites: There is at least 1 person in the list.
Test case:
list
Expected: Show a list of all person in InsureBook, and details are displayed in the status message.
Locating persons by keyword
Locating persons from the list by using keyword
Prerequisites: There is at least 1 person in the list which matches with the keyword that is being tested.
Test case:
find n/John
Expected: Show the quantity and list of people who matches the keyword, sorted by name, partial matches is considered a success, and details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
find t/friends t/colleagues s/tag
Expected: Show the quantity and list of people who matches the keyword, sorted by number of tag, only exact matches is considered a success, and details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
find n/bernice n/david
Expected: Show the quantity and list of people who matches the keyword, sorted by name, partial matches is considered a success, and details are displayed in the status message.Test case:
find
Expected: list of person is not updated. Error details are displayed in the status bar and command entered stays in the command box.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
find 0,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Locating persons from the list by using keyword that does not match
Prerequisites: All persons in the list does not match with the keyword that is being tested.
Test case:
find n/bob
Expected: No one is listed, and details are displayed in the status message.
Viewing help
Show help
- Test case:
help
Expected: New window is opened with the link to InsureBook's UserGuide, and details are displayed in the status message.
- Test case:
Clearing InsureBook entries
Clear existing list of person in InsureBook
- Test case:
clear
Expected: All person in list is removed, and details are displayed in the status message.
- Test case:
Exiting InsureBook
Exit InsureBook
- Test case:
exit
Expected: InsureBook successfully closes.
- Test case: